PETG vs. PLA 3D Printing Material Comparison—How to Make the Best Choice for Your Project?
In the world of 3D printing, selecting the right material is the crucial first step toward successful printing. For beginners and experts alike, PLA and PETG are undoubtedly two of the most popular and widely used materials. But which one is better suited for your specific project? This article will delve into comparing the performance, printability, and application scenarios of PETG and PLA to help you make an informed decision.
Foundational Knowledge: What Are They?
PLA (Polylactic Acid): A bio-based, biodegradable material derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane. Its ease of printing, odorlessness, and eco-friendly properties make it the absolute go-to choice for beginners. It offers a pleasant printing experience with an extremely high success rate.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Essentially a modified version of the PET material found in everyday water bottles, where the “G” stands for “glycol modification,” making it easier to print. It combines PLA’s printability with ABS’s durability, often regarded as an advanced, “all-purpose” material.
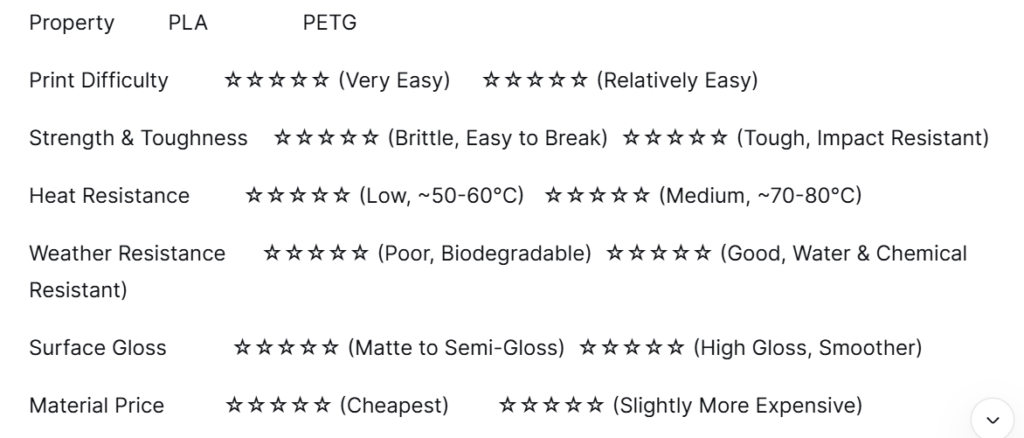
PETG vs PLA 3D Printing Material Performance Comparison
In-Depth Analysis:
Printing Experience and Adhesion:
PLA: Compatible with nearly all FDM printers. Offers excellent adhesion, typically requiring only masking tape or a PEI sanding board for flawless prints with minimal warping. Requires lower printing temperatures (190-220°C).
PETG: Slightly more challenging to print than PLA but far easier than ABS. Its main challenge lies in excessive adhesion—it sticks strongly to the heated bed (recommended to use a glue stick or specialized coating for easy removal) while exhibiting some stringing tendencies, requiring careful retraction settings calibration.

Mechanical Properties and Durability:
PLA’s primary drawback is brittleness. It offers high stiffness but lacks toughness, making it prone to shattering upon impact or dropping. Consequently, it is unsuitable for functional parts requiring stress resistance or bending.
PETG’s core strength lies in its exceptional toughness and impact resistance. It can bend and absorb energy without fracturing, making it ideal for tool handles, protective covers, moving parts, and similar applications.

Environmental Resistance:
PLA’s biodegradability is a double-edged sword. In humid or outdoor environments, it may gradually become brittle and degrade. Additionally, its low glass transition temperature means summer car interiors can cause PLA parts to soften and deform.
PETG offers outstanding water resistance, chemical resistance (resistant to oils, weak acids, and weak alkalis), and superior heat resistance, making it highly suitable for outdoor gear, hydroponic planters, automotive interior components, and similar applications.
How to Choose? Application Scenario Guide
Choose PLA :
You are a beginner new to 3D printing.
Your project involves display models, toys, artwork, or educational prototypes.
You require extensive support structures (PLA supports are easier to remove).
You prioritize optimal print detail and surface quality (PLA typically excels in fine detail reproduction).
Choose PETG :
You need functional parts, tools, or machine components.
Your creations will be used outdoors or exposed to water/chemicals (e.g., garden ornaments, pipe fittings).
Parts require flexibility and impact resistance (e.g., phone cases, snap fasteners).
You require better heat resistance than PLA offers (e.g., car phone mounts).
Conclusion-PETG vs. PLA 3D Printing Material Comparison
In summary, there is no absolute winner between PLA and PETG—only the choice that best fits your needs.
PLA is the perfect “entry-level mentor” and “model specialist,” conquering most everyday and non-load-bearing applications with unmatched printability and beautiful surface finishes.
PETG, the reliable “all-round engineer,” bridges the gap between PLA and more advanced materials like ABS or nylon with superior durability and environmental resistance, making it an excellent choice for functional applications.
We recommend every user start building experience with PLA before tackling PETG. Once you master PETG’s calibration techniques, it will likely become the most reliable and frequently used “workhorse” in your material library. May this comparison guide your precise decisions and help you print more perfect creations!