Functional 3D Printing Project
Beyond Prototyping: How Functional 3D Printing Projects Are Revolutionizing Design and Manufacturing
In many people’s minds, 3D printing remains a tool for creating plastic models and prototypes. Yet a technological wave has propelled this technology to entirely new heights—functional 3D printing projects are quietly transforming how engineers, manufacturers, and even DIY enthusiasts solve problems. It’s no longer about “what it looks like,” but “what it can do.” This article explores the core advantages of functional 3D printing and demonstrates its immense value from home workshops to industrial production lines.
What Is Functional 3D Printing?
Functional 3D printing refers to using additive manufacturing to create end-use parts with practical applications. These components must withstand mechanical stress, thermal forces, or specific environmental conditions and integrate directly into final products or systems. Success hinges on precise control over material properties, structural design, and printing processes.
Why Choose 3D Printed Functional Parts? Core Advantages Explained
Unparalleled Design Freedom and Integration
Traditional manufacturing (e.g., milling, injection molding) is constrained by tool paths and molds, whereas 3D printing can achieve virtually any geometry. This enables engineers to design topologically optimized structures that significantly reduce weight while maintaining strength, or consolidate multiple components into a single printed part—eliminating assembly steps and reducing failure points. For example, a printed drone mount can incorporate intricate internal cooling channels—a feat challenging to achieve with conventional methods.
Rapid Iteration and On-Demand Production
From design to physical part, 3D printing takes only hours. This enables development teams to rapidly test, fail, learn, and refine, drastically shortening product development cycles. For niche demands or discontinued equipment, spare parts can be produced on demand without investing in costly molds, significantly reducing inventory costs and downtime. Many companies are leveraging this technology to establish “digital inventories,” storing only CAD files to print required parts anytime.
Cost Efficiency and Customization
For small-batch, complex-structure parts, 3D printing often offers greater cost advantages than traditional manufacturing. It paves the way for mass customization: from medical orthotics perfectly fitted to patients’ bodies to cockpit control components tailored for race car drivers, functional 3D printing makes personalization affordable.
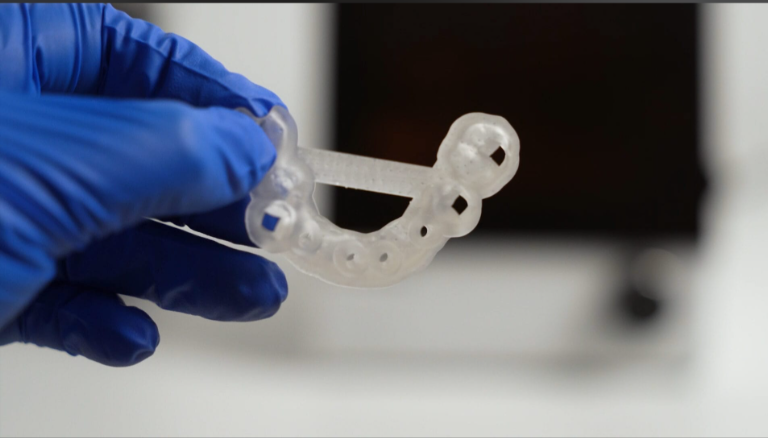

Successful Applications of Functional 3D Printing
Aerospace & Automotive: Manufacturing lightweight brackets, fixtures, jigs, and high-temperature-resistant internal engine test components.
Medical Field: Production of surgical guides, customized implants (e.g., acetabular cups), and biocompatible prosthetic sockets that directly improve patient quality of life.
Industrial Manufacturing: Printing customized end-of-arm tooling, robust fixtures, and replacement parts resistant to wear and chemicals.
Research & Robotics: Rapidly prototype and manufacture robotic joints, gears, sensor housings, and more, accelerating open-source robotics projects.
Daily Life: From repairing high-strength gears in household appliances to crafting bespoke tool organizers for kitchens or workshops, functional 3D printing empowers everyone to become a “problem-solving master.”

Kickstart Your Project: Material Selection is Key
Successful functional projects hinge on choosing the right materials:
ASA/ABS: Excellent weather resistance and mechanical strength, ideal for outdoor applications.
Nylon (PA): High strength, toughness, and wear resistance—perfect for gears and snap-fit components.
PETG: Offers a balanced trade-off between strength, toughness, and printability, with chemical resistance.
Polycarbonate (PC): Exceptional strength and heat resistance for demanding environments.
Composite Materials: Filaments reinforced with carbon fiber or glass fiber further enhance part stiffness, strength, and heat resistance.
Conclusion-Functional 3D Printing Project
Functional 3D printing has transcended “rapid prototyping” to become a powerful manufacturing tool. By unlocking design potential, accelerating innovation cycles, and enabling cost-effective customization, it is reshaping how we create and repair objects. Whether you’re a professional engineer or a passionate creator, embracing functional 3D printing means embracing a future manufacturing approach with limitless possibilities.
Start your next project today, transforming digital designs into robust, reliable solutions, and experience the manufacturing revolution firsthand.